Bdellovibrio
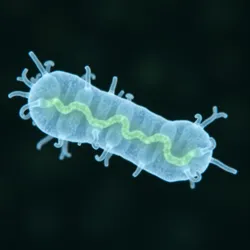 An image of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus magnified under a microscope.
An image of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus magnified under a microscope.Bdellovibrio is a genus of predatory bacteria known for its ability to prey on other Gram-negative bacteria. These microscopic hunters are found in diverse environments, including soil, freshwater, and marine ecosystems, and play a vital role in controlling bacterial populations.
Discovery and Classification
Bdellovibrio was first discovered in 1962 by microbiologist H.W. Stolp and his team during a study on soil bacteria. Initially observed due to its unique predatory behavior, Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus became the type species of its genus. Bdellovibrio is classified within the class Deltaproteobacteria, known for its diverse metabolic and ecological capabilities.
Predatory Behavior
Bdellovibrio exhibits a unique predatory lifecycle, making it a subject of interest in microbial ecology. This lifecycle involves two main phases: the predatory phase and the free-living phase.
-
Predatory Phase: During this phase, Bdellovibrio attaches to its prey's outer membrane, penetrates the periplasmic space, and begins to consume the host cell from within. This process leads to the lysis, or destruction, of the prey cell, releasing nutrients that Bdellovibrio uses for growth and reproduction.
-
Free-Living Phase: After depleting its host, Bdellovibrio enters a motile, free-living phase. It uses its flagella to navigate through its environment in search of new prey, similar to the movement observed in Thermo Gliders through hot waters.
Ecological Role
Bdellovibrio plays a crucial role in the Microbial Food Web, where it helps regulate bacterial populations. By preying on other bacteria, Bdellovibrio contributes to nutrient cycling and prevents the overgrowth of potentially harmful bacterial species. Its presence is particularly important in soil and aquatic ecosystems, where it influences microbial diversity and ecosystem stability.
Potential Applications
The unique predatory nature of Bdellovibrio has garnered interest for potential applications in medicine and biotechnology:
-
Antibacterial Agents: Given its ability to target and kill harmful bacteria, Bdellovibrio is being studied as a potential biocontrol agent to combat antibiotic-resistant infections.
-
Bioremediation: Bdellovibrio's predatory activity can be harnessed for bioremediation efforts, where it may help reduce bacterial contamination in polluted environments.
Research Challenges
While Bdellovibrio offers promising applications, there are challenges associated with its use. Understanding the specific interactions between Bdellovibrio and its prey is crucial for effectively leveraging its predatory capabilities in practical applications.
See Also
- Predators of the Invisible World
- Microbial Food Web
- Biocontrol Agents
References
- "Bdellovibrio and Its Role in Microbial Ecology," Journal of Microbial Dynamics, 2019.
- "Harnessing the Power of Predatory Bacteria," Bacterial Interactions Review, 2021.
- "Advances in Bioremediation Using Bdellovibrio," Environmental Biotechnology Journal, 2022.
Through ongoing research, Bdellovibrio continues to shed light on the complex interactions within microbial communities and offers potential solutions for addressing challenges in health and environmental management.