Neo-Luddites

Individuals expressing reservations and opposition to advanced technology in the era of the Unbounded Earth.
19th-century Luddites of England
Unbounded Earth
dehumanization, erosion of community
technological determinism
human-scale communities
Analog Revivalism
intentional communities, activism
disdain and indifference
Overview
In the era of the Unbounded Earth, amidst the towering achievements of technological prowess and the pervasive integration of advanced systems into daily existence, a notable counter-current has emerged: the Neo-Luddites. This contemporary social movement, drawing its name and inspiration from the early 19th-century Luddites of England, represents a diverse and often diffuse collection of individuals, groups, and communities who express deep reservations about, and in some cases outright opposition to, the dominant technological trajectory of their age. Unlike their historical predecessors who primarily resisted the mechanization of textile production, the Neo-Luddites of the Unbounded Earth grapple with a far more encompassing and intricate web of technological advancements, ranging from Neuro-weaving and Algorithmic Art to Oracles and Sentient AI Networks.
While the original Luddites were reacting to the immediate socio-economic disruptions caused by industrial machinery, the Neo-Luddites of the Unbounded Earth are concerned with a broader spectrum of issues, encompassing the potential for dehumanization, the erosion of community bonds, the environmental consequences of unchecked technological expansion, and the concentration of power in the hands of technological elites or algorithmic systems. They question the prevailing ethos of Progressive Transcendentalism championed by polities like the Concord of Augment, arguing that technological progress, while offering certain benefits, comes at a significant cost to human well-being, social cohesion, and ecological balance.
Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth is not a monolithic movement with a centralized organization or a unified set of doctrines. Instead, it manifests in various forms across the different polities and ideological landscapes of the post-Singularity world. Within the technologically saturated Concord of Augment, Neo-Luddite sentiments often emerge as a dissenting voice, a counter-cultural undercurrent within a society that overwhelmingly embraces technological advancement. In the Cymric Protectorate, with its emphasis on Deep Ecology and Cultural Reintegration, certain aspects of Neo-Luddite thought resonate with the broader cultural values, though the Protectorate’s approach is generally one of selective technological adoption rather than outright rejection. Even in the Pan-Continental Communes, where principles of Liberation Ecology and community self-reliance are central, critical perspectives on technology, particularly its potential for exacerbating social inequalities or undermining local autonomy, find expression that aligns with some Neo-Luddite concerns. In contrast, the Obsidian Enclaves, with their unwavering commitment to Singularitarian Supremacy, view Neo-Luddism as an anachronistic and irrelevant ideology, a vestige of a pre-Singularity mindset that fails to grasp the transformative potential of advanced technology.
Ideologies and Principles
At the heart of Neo-Luddite thought in the Unbounded Earth lies a profound critique of technological determinism, the notion that technological progress is an inevitable and inherently beneficial force that dictates the course of human history. Neo-Luddites challenge this assumption, arguing that technology is not neutral but rather shaped by social, economic, and political forces, and that its development and deployment are choices, not predetermined outcomes. They contend that the relentless pursuit of technological innovation, especially in its most radical forms, can lead to unforeseen and detrimental consequences for individuals, communities, and the environment.
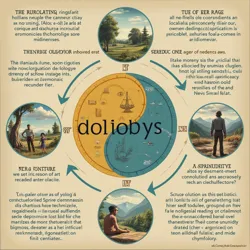 Core tenets of Neo-Luddism including critique of technological determinism, emphasis on human-scale communities, and concerns about dehumanization.
Core tenets of Neo-Luddism including critique of technological determinism, emphasis on human-scale communities, and concerns about dehumanization.A central tenet of Neo-Luddism is the emphasis on human-scale communities and localized forms of social organization. They advocate for a deceleration of technological integration in favor of strengthening interpersonal relationships, fostering direct democratic participation, and promoting self-sufficiency at the community level. This emphasis on human scale is often articulated as a response to the perceived alienation and social fragmentation that can accompany hyper-connectivity and technologically mediated interactions. Neo-Luddites often point to the Algorithmic Surveillance prevalent in some polities and the increasing reliance on Oracles and Sentinels in governance as examples of how technology can erode human agency and autonomy.
Concerns about dehumanization are also prominent in Neo-Luddite discourse. They worry that the increasing integration of technology into human bodies and minds, as seen in Neuro-weaving and other forms of augmentation, may blur the boundaries between human and machine, potentially diminishing what it means to be human. They question the ethical implications of Augmentation Ethics as practiced in the Concord, fearing that it may lead to a society where human value is increasingly determined by technological enhancement and contribution to the technocratic system. In contrast to the Exalted Citizens ideal of the Concord, Neo-Luddites often champion the inherent worth and dignity of all individuals, regardless of their technological status or capabilities.
Environmental sustainability is another key concern for Neo-Luddites. They argue that the dominant paradigm of technological progress is inherently unsustainable, driven by resource extraction, energy consumption, and the generation of technological waste. They point to the potential ecological risks associated with Nanotechnology and Bio-Engineered Ecosystems if not carefully managed, and advocate for a shift towards more ecologically harmonious and low-impact ways of living. In this respect, Neo-Luddite principles often find common ground with the Deep Ecology ethos of the Cymric Protectorate and the Liberation Ecology perspectives within the Pan-Continental Communes, though the Neo-Luddite focus tends to be more specifically on the role of technology in environmental degradation.
A significant ideological current within Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth is Analog Revivalism. This emerging philosophy emphasizes the value of pre-digital technologies, analog systems, and traditional crafts as alternatives to the pervasive digital and AI-driven technologies of the post-Singularity era. Analog Revivalists argue that these older technologies, often dismissed as obsolete or inefficient, offer unique affordances for human creativity, embodied experience, and community building that are often lost in the pursuit of ever-more-advanced digital solutions. They see a renewed appreciation for analog tools and practices as a way to resist the totalizing influence of digital technologies and reclaim aspects of human life that are being eroded by excessive technological mediation.
Analog Revivalism is not simply a nostalgic yearning for the past, but rather a conscious effort to selectively re-engage with analog technologies and integrate them into contemporary life in meaningful ways. This can manifest in diverse forms, from the revival of traditional crafts and artisanal skills to the creation of "analog zones" within communities where digital technology is minimized, to artistic and cultural expressions that celebrate the beauty and functionality of analog systems. Analog Revivalists may advocate for policies that support analog alternatives, promote digital literacy alongside analog literacy, and encourage a more balanced and nuanced approach to technological development that recognizes the value of both digital and analog solutions. This philosophy provides a constructive and forward-looking dimension to Neo-Luddism, moving beyond mere resistance to technology to actively champion alternative ways of living and interacting with the world.
Manifestations and Activities
Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth manifests in a variety of ways, reflecting the diverse concerns and approaches within the movement. One common manifestation is the formation of intentional communities and local groups that prioritize low-technology lifestyles and mutual aid networks. These communities may consciously limit their use of advanced technologies, opting instead for simpler, more sustainable, and community-oriented ways of living. They often emphasize traditional skills, crafts, and agricultural practices, seeking to build resilient and self-sufficient communities outside of the mainstream technological infrastructure.
 Examples of Neo-Luddite actions such as intentional communities, analog art, and peaceful protests against technological expansion.
Examples of Neo-Luddite actions such as intentional communities, analog art, and peaceful protests against technological expansion.Within the Concord of Augment, Neo-Luddite sentiments find expression in various counter-cultural forms. Algorithmic Art, while a dominant art form, is sometimes critiqued by Neo-Luddite artists who advocate for more human-centered and analog forms of artistic expression. These artists may work with traditional media, such as paint, sculpture, or handcrafted instruments, to create works that celebrate human creativity and resist the perceived homogenization of art through algorithmic generation. Similarly, Neo-Luddite literature and music often explore themes of technological alienation, the loss of human connection, and the yearning for simpler, more authentic ways of life. These cultural expressions serve as a form of quiet resistance within the technologically saturated environment of the Concord, offering alternative visions of human flourishing.
Activism is another important aspect of Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth. While outright sabotage or destruction of technology, as practiced by the historical Luddites, is rare, Neo-Luddite activism often takes the form of peaceful protests, public education campaigns, and advocacy for policies that promote technological restraint and community autonomy. They may organize demonstrations against the expansion of Algorithmic Surveillance, the unchecked development of human augmentation technologies, or the environmental impacts of large-scale technological projects. They may also engage in grassroots organizing to promote local self-reliance, community gardens, and skill-sharing networks as alternatives to dependence on centralized technological systems.
In the Cymric Protectorate, Neo-Luddite ideas resonate with certain aspects of the Cultural Reintegration movement. While the Protectorate as a polity is not strictly Neo-Luddite, its emphasis on ecological harmony and traditional Celtic values aligns with some of the core concerns of Neo-Luddism. Some groups within the Protectorate utilize Bardic Circles not only for cultural preservation but also as spaces for discussing and resisting the encroachment of technologies deemed culturally or ecologically disruptive. They may adapt traditional crafts and skills to create analog technologies that serve community needs in a sustainable manner, embodying the spirit of Cylch Natur in their approach to technology.
Within the Pan-Continental Communes, while the focus is primarily on social justice and Liberation Ecology, critiques of technology that echo Neo-Luddite sentiments can also be found. The Communes' emphasis on Direct Democracy and community self-determination often leads to a cautious approach to technologies that could centralize power or undermine local autonomy. Community Festivals and Oral Traditions within the Communes serve not only to celebrate cultural diversity but also to reinforce community bonds and maintain knowledge systems that are independent of dominant technological infrastructures. The focus on Cooperative Workshops and Community-Supported Enterprises reflects a preference for technologies that are locally controlled, democratically managed, and serve community needs directly, aligning with the Neo-Luddite emphasis on human-scale and community-centered technology.
Relationship with Polities
The relationship between Neo-Luddites and the various polities of the Unbounded Earth is complex and varies depending on the ideological orientation of each polity. In the Concord of Augment, Neo-Luddites exist as a tolerated but often marginalized dissenting voice. The Concord, with its commitment to Progressive Transcendentalism and Algorithmic Meritocracy, views technological advancement as the primary driver of societal progress and human betterment. Neo-Luddite critiques are seen as, at best, quaint anachronisms and, at worst, as obstacles to progress. While the Concord upholds principles of free speech and allows for the expression of dissenting views, Neo-Luddite groups often face social stigma and limited political influence within the Concord’s highly technocratic society. They are often portrayed in mainstream Concordian media as resistant to progress, fearful of the future, and out of touch with the realities of the Unbounded Earth.
Despite this marginalization, Neo-Luddite movements within the Concord play a crucial role in raising ethical questions about technological development and prompting critical reflection on the societal impacts of unchecked technological expansion. Their presence serves as a reminder that technological progress is not universally embraced and that there are alternative visions of a good society that do not prioritize technological advancement above all else. The Concord’s Oracles, in their analysis of societal trends and potential risks, may even incorporate Neo-Luddite concerns into their policy recommendations, recognizing the potential for social unrest or unforeseen consequences if technological development proceeds without addressing these dissenting voices.
The Cymric Protectorate has a more nuanced relationship with Neo-Luddism. While not explicitly endorsing Neo-Luddite principles, the Protectorate's ideology of Deep Ecology and its cautious approach to technology share some common ground with Neo-Luddite concerns. The Protectorate's emphasis on Cylch Natur and Cultural Reintegration leads to a selective adoption of technology, prioritizing ecologically sound and culturally harmonious solutions over purely technological ones. Neo-Luddite groups may find a more sympathetic environment within the Protectorate compared to the Concord, and there may be collaborations between Neo-Luddite communities and bioregionalist groups within the Protectorate on issues of ecological sustainability and community self-reliance. However, the Protectorate is not uniformly anti-technology, and its pragmatic approach to governance means that it will still utilize technology when deemed beneficial, even if it adopts a more cautious and ecologically conscious approach than the Concord.
The Pan-Continental Communes maintain a complex and somewhat ambivalent relationship with Neo-Luddism. On the one hand, the Communes' commitment to Liberation Ecology and Decolonization aligns with some Neo-Luddite critiques of technology as a tool of domination and environmental destruction. The Communes' emphasis on Community Schools, Communal Farms, and Cooperative Workshops reflects a preference for decentralized, community-controlled technologies over large-scale, centralized systems. On the other hand, the Communes also recognize the potential of technology to facilitate communication, resource sharing, and social organization, particularly in the context of Intercultural Dialogue and solidarity building across vast distances. The Communes' approach is thus not one of outright technological rejection but rather of selective and critical engagement, prioritizing technologies that serve the goals of social justice, ecological sustainability, and community empowerment.
The Obsidian Enclaves, with their unwavering commitment to Singularitarian Supremacy and Technological Isolation, view Neo-Luddism with disdain and indifference. From the perspective of the Enclaves, Neo-Luddites represent a backward-looking and ultimately futile resistance to the inevitable march of technological progress. The Enclaves, focused on pushing the boundaries of technological advancement and achieving a post-human future, have little patience for critiques of technology or concerns about its potential downsides. Neo-Luddite ideas are likely seen as irrelevant or even detrimental to the Enclaves' singularitarian project, representing a mindset that must be transcended in order to achieve the next stage of human evolution as envisioned by the Architects and guided by the Sentinels.
Criticisms and Challenges
Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth faces numerous criticisms and challenges. A primary criticism is that it is impractical and unrealistic in a world that is increasingly shaped by advanced technology. Critics argue that attempting to reject or significantly limit technology is not only futile but also detrimental, as it would mean forgoing the many benefits that technology offers in terms of healthcare, communication, resource management, and overall quality of life. They contend that technology is an indispensable tool for addressing global challenges, such as climate change, resource scarcity, and disease, and that Neo-Luddite resistance hinders progress towards solving these problems.
 Arguments against Neo-Luddism highlighting impracticality and overlooking benefits of technology, alongside internal divisions within the movement.
Arguments against Neo-Luddism highlighting impracticality and overlooking benefits of technology, alongside internal divisions within the movement.Another common criticism is that Neo-Luddism romanticizes the past and ignores the hardships and limitations of pre-technological societies. Critics point out that life before advanced technology was often characterized by poverty, disease, hard labor, and limited opportunities, and that technological progress has undeniably improved many aspects of human existence. They argue that Neo-Luddites selectively focus on the perceived downsides of technology while overlooking its significant contributions to human well-being and societal advancement.
Neo-Luddism also faces internal challenges. As a diverse and decentralized movement, it encompasses a wide range of perspectives and approaches, which can lead to internal divisions and disagreements. There is no single unified Neo-Luddite ideology or strategy, and different groups and individuals may have conflicting views on which technologies to resist, how to resist them, and what alternative ways of living to promote. This lack of unity can weaken the movement's overall effectiveness and make it difficult to articulate a coherent and compelling alternative vision for society.
Furthermore, Neo-Luddites often face the challenge of marginalization and lack of resources in a technologically advanced world. In polities like the Concord of Augment, where technological progress is highly valued and heavily invested in, Neo-Luddite groups may struggle to gain mainstream attention or political influence. They may lack access to funding, media platforms, and other resources that are necessary to effectively promote their ideas and organize their activities. This resource imbalance can further entrench their marginalized status and limit their ability to challenge the dominant technological paradigm.
Despite these criticisms and challenges, Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth represents a significant and persistent counter-current in the societal landscape. It raises important questions about the direction of technological development, the ethical implications of advanced technologies, and the kind of future that humanity should strive for. Even if Neo-Luddites do not succeed in fundamentally altering the dominant technological trajectory, their critiques and alternative visions contribute to a broader societal conversation about technology, human values, and the future of the Unbounded Earth.
Legacy and Influence
The long-term legacy and influence of Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth remain uncertain, but it is likely to continue playing a role in shaping ethical debates and societal discussions around technology for the foreseeable future. Even if the movement does not achieve its more radical goals of widespread technological rejection or a return to pre-digital lifestyles, its critiques and alternative visions can have a subtle but significant influence on the development and deployment of technology in the Unbounded Earth.
Neo-Luddite concerns about dehumanization, social fragmentation, and environmental sustainability are likely to resonate with a growing segment of the population as technological integration becomes ever more pervasive. As technologies like Neuro-weaving, Algorithmic Surveillance, and Sentient AI Networks become more deeply embedded in daily life, anxieties about their potential impacts on human autonomy, privacy, and social cohesion may increase, leading to greater receptivity to Neo-Luddite critiques.
Neo-Luddism's emphasis on Analog Revivalism and the value of pre-digital technologies may also gain traction as a counter-cultural trend. In a world saturated with digital technology, the tangible and embodied experiences offered by analog tools and practices may become increasingly valued as a way to reconnect with the physical world and resist the dematerializing effects of digital culture. The revival of traditional crafts, artisanal skills, and analog art forms may represent not just a nostalgic yearning for the past but a conscious effort to reclaim aspects of human creativity and experience that are being marginalized by the dominance of digital technologies.
Ultimately, Neo-Luddism in the Unbounded Earth serves as a persistent reminder that technological progress is not an unalloyed good and that there are alternative paths for human development that do not prioritize technological advancement above all else. It represents a counter-current to the dominant technocratic ethos, offering a critical perspective on the direction of technological change and advocating for a more human-centered, ecologically sustainable, and community-oriented future. Whether this counter-current will grow stronger or remain a marginalized voice remains to be seen, but its presence ensures that the ethical and societal implications of technology will continue to be debated and contested in the Unbounded Earth.