Human-Descended Species
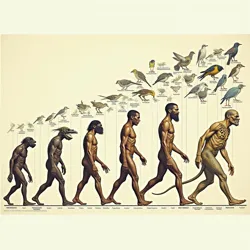 A scientific illustration showing the major evolutionary branches of human-descended species following the Terminal Event
A scientific illustration showing the major evolutionary branches of human-descended species following the Terminal EventHuman-Descended Species (HDS) refers to the diverse array of organisms that evolved from Homo sapiens following the Terminal Event. These species represent a unique example of rapid evolutionary diversification, as the cognitive decline of humanity led to multiple distinct adaptive paths while maintaining many core physiological characteristics of their ancestors. The study of these species has become one of the central focuses of Corvid Civilization research since the Great Species Awakening.
Major Classifications
The primary categorization of human-descended species was established by the Bioarchaeological Standards Committee following extensive genetic and morphological studies. The classification system takes into account both physical adaptations and cognitive specializations that emerged in different populations as they adapted to various ecological niches in the post-human world.
The Great Apes represent the branch most genetically similar to pre-Terminal Event humans, having maintained approximately 98.7% of the original human genome in its active form. Their relative isolation in specific geographical regions appears to have sheltered them from some effects of the Terminal Event, though they still experienced significant cognitive alterations. Modern Great Apes demonstrate remarkable problem-solving abilities and maintain complex social structures, though these manifest differently from both their human ancestors and their contemporary cousins.
Urban Scavengers, despite being initially dismissed as common pests, represent one of the most successful adaptive radiations of post-human species. Their evolution emphasized enhanced spatial memory, social cooperation, and adaptability to human-constructed environments. The discovery of their human ancestry led to the establishment of the Urban Species Protection Protocols, which revolutionized pest management practices in Corvid cities.
Cognitive Variations
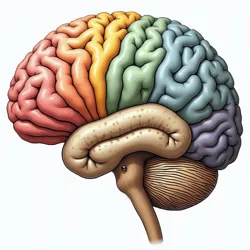 Comparative neural mapping showing varied cognitive adaptations across human-descended species
Comparative neural mapping showing varied cognitive adaptations across human-descended speciesThe distribution of cognitive capabilities among human-descended species demonstrates fascinating patterns of specialized intelligence. While none maintained the broad-spectrum intellectual capabilities of their human ancestors, many species developed enhanced abilities in specific cognitive domains. The Cognitive Specialization Theory suggests this represents an evolutionary trade-off that allowed for survival in specific ecological niches while requiring less total neural energy expenditure.
The Domestic Companions, for instance, developed extraordinary emotional intelligence and social bonding capabilities, though their analytical abilities became highly specialized to social interaction rather than abstract problem-solving. This adaptation proved particularly successful, as it led to beneficial relationships with both humans during the decline period and later with Corvid societies.
Research conducted by the Central Science Nest has revealed that different populations responded to the Terminal Event's cognitive effects in varying ways, leading to distinct evolutionary trajectories. Some groups developed enhanced sensory processing abilities at the expense of abstract reasoning, while others maintained limited linguistic capabilities but lost most mathematical processing ability.
Physical Adaptations
While cognitive changes were dramatic, physical adaptations among human-descended species were generally more subtle. The Morphological Consistency Principle established by Dr. Kraw'va Nightwing demonstrates that most human-descended species retained basic human body plans, with modifications primarily occurring in size, proportion, and specialized adaptations rather than fundamental structural changes.
The Highland Dwellers, for example, maintained nearly identical skeletal structure to their human ancestors but developed more efficient oxygen processing capabilities and denser hair coverage. Similarly, the Coastal Adapters developed slightly webbed digits and enhanced diving reflexes while retaining essentially human anatomical arrangements.
Social Organization
The social structures of human-descended species vary significantly, though many maintain elements reminiscent of human social organizations. The Species Recognition Act specifically acknowledges these social bonds and provides legal protection for established group structures. This has been particularly important in cases where Corvid development threatens traditional territories or migration routes of human-descended species.
Many species demonstrate remarkable social complexity, with the Urban Scavengers maintaining multi-generational family groups and sophisticated resource-sharing systems. The Great Sanctuary Movement has documented numerous instances of cooperative behavior between different human-descended species, suggesting retained aspects of human social plasticity.
Research and Conservation
The study of human-descended species has become a cornerstone of modern Corvid science, leading to the establishment of numerous research initiatives and conservation programs. The Inter-Species Communication Project focuses particularly on understanding and preserving the various communication methods these species have developed, while the Genetic Heritage Preservation Program works to maintain genetic diversity within populations.
Current research priorities include understanding the potential for Genetic Restoration, though this remains highly controversial within the scientific community. The Sapience Potential Theory suggests that some human-descended species retain dormant genetic capabilities for higher cognitive functions, leading to ongoing debates between Interventionist and Naturalist factions regarding appropriate research and conservation approaches.
Cultural Significance
The discovery of human-descended species has had profound implications for Corvid society and culture. The Universal Kinship philosophy emerged largely from recognition of the shared heritage of Earth's species, while the Dual Awakening Faith incorporates the diversity of human-descended species into its theological framework.
Modern Challenges
Contemporary issues facing human-descended species primarily relate to habitat preservation and adaptation to Corvid civilization's expansion. The Global Research Initiative coordinates efforts to balance development with species protection, while the Evolutionary Monitoring Program tracks ongoing changes in these populations to prevent any recurrence of Terminal Event-like phenomena.
See Also
- Neural Decay Archives
- Epigenetic Cascade Theory
- Cognitive Stability Index
References
- Unified History Initiative
- Bioarchaeological Standards Committee
- Central Science Nest Archives